Flow Accelerator was overjoyed to meet Sabrina Salameh, Seedstars’ Head of MENA Partnerships, and an Egyptian fellow entrepreneurship enthusiast from France, eager to share her knowledge and bright spirit to entrepreneurs across the world.
During her visit to Palestine, Sabrina wanted to give back to the aspiring entrepreneurs of Palestine and leave her imprint, and she accomplished just that in her exciting and fruitful “Inside the Entrepreneurial Mindset” workshop hosted at Flow Accelerator. Sabrina brought our audience’s attention to the concept of “entrepreneurial mentality,” a concept with which they were likely already familiar, but from a unique angle. Throughout the session, she also introduced them to the topic of the future of work and the skills that everyone should strive to acquire in order to maintain an ongoing productivity and provide value to the world.

Who is Seedstars?
Seedstars an international investment and education Swiss company that has a goal to change people’s lives across Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, Central-Eastern Europe, and Asia. Through entrepreneurship and technology, Seedstars support the world’s most ambitious and dedicated entrepreneurs in growing and scaling their companies to create meaningful and lasting change.
They work in partnership with governments, development agencies, corporates, and private donors to develop emerging market ecosystems, create local jobs and fuel regional income growth through businesses that tackle impactful problems.
The Future of Work
To understand how we got to where we are today, Sabrina explained the evolution of the industrial revolution to emphasize on where the main value lies in this day of age when it comes to the workforce.
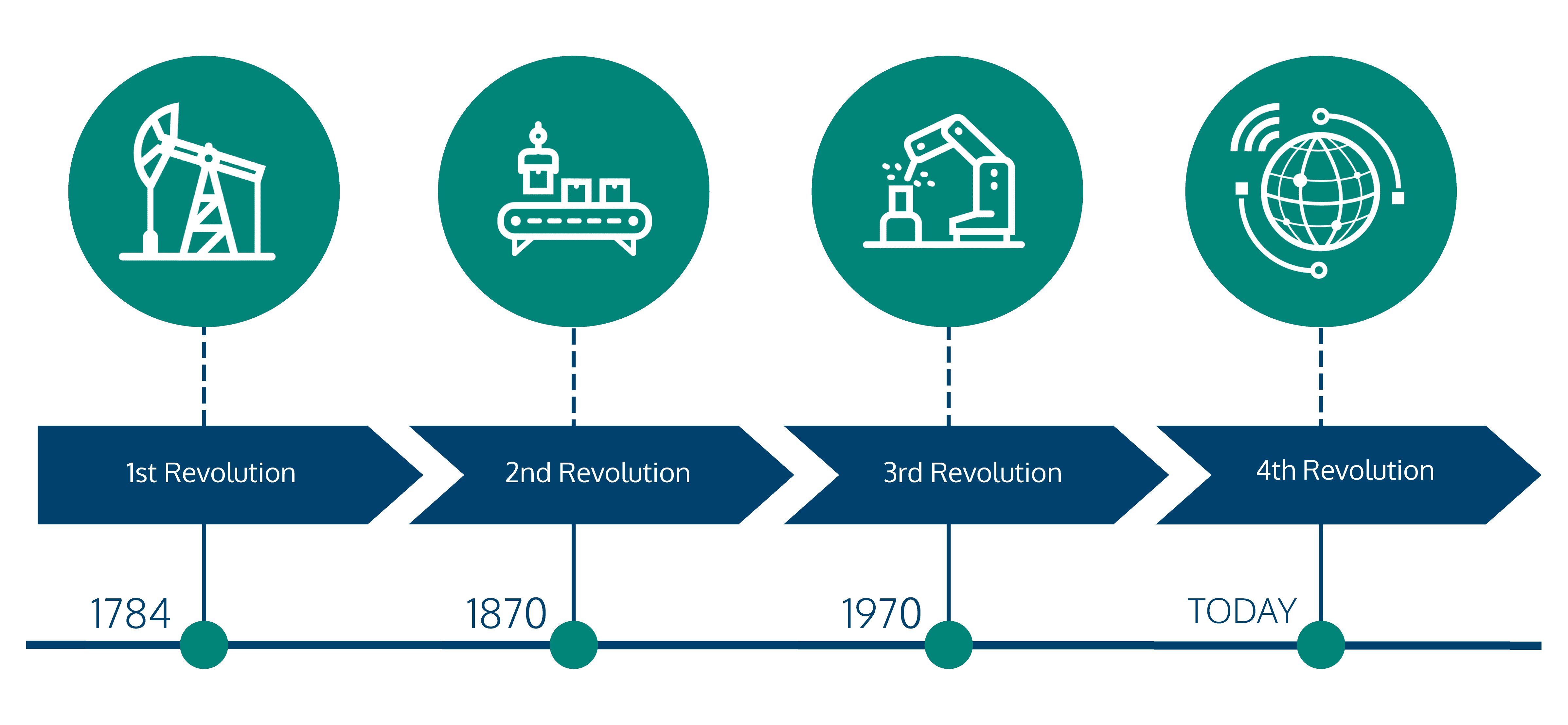
The Evolution of the Revolution
The 1st Industrial Revolution Mainly dealt with the textile and metallurgical sectors, with the introduction of the steam engine in the second half of the 18th century. The 2nd Industrial Revolution started with the introduction of electricity, chemicals, and oil. It played a huge role in the massive adoption of electronics, telecommunications, and information technology in the following industrial revolution. The 3rd Industrial Revolution, also known as the digital revolution, it coincides with the transition from mechanics, electrical and analog technologies to digital technology, linked to the birth of computers, robots, the first spacecraft and satellites. The 4th Industrial Revolution, known as “Factory 4.0” or “Business 4.0”, it owes its name to a 2011 initiative by large companies and research centers with the aim of increasing the competitiveness of manufacturing industries, through the growing integration of “cyber-physical systems” (as known as CPS), in industrial processes. The 4th industrial revolution is pushing automation to new heights, blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological spheres, and relying on technology to do work that was traditionally performed by humans. Changes in employment and business across all sectors are inevitable as a result of this new industrial revolution. Although many businesses and jobs may vanish, many more will spring up at the same time.
Reskill to Survive
The fourth Industrial Revolution has shown the possibility of disrupting entire industries and trigger massive job loss with the increased reliance on technological innovations, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and 3D printing.
Though individual sectors and companies will experience layoffs, it is expected most economies will generate new jobs in the years ahead due to emergence of different types of careers, new sources of demand and right-skilled workforces emerge. This new era calls for significant “right-skilling” – retraining your workforce and acquiring people with the right skills to fill the gaps. To overcome the unprecedented skills crisis, people should recognize that they must adapt to change and begin actively forging reskilling initiatives. Self-direction is also necessary to discover new promising work opportunities and to reskill.

What are the Skills of Tomorrow?
Sabrina mentioned in the session, that the future lies in the capabilities we bring on the table through the soft skills that are not found in classrooms, as it’s not about learning and memorizing anymore.

The rapidly changing future doesn’t only affect the traditional workforce! The need for forward-thinking reskills will become a necessity to survive in this technology dominated age not only for employees and corporates, but startups, and entrepreneurs as well!
Technology is not the enemy! The possibilities of billions of people connected by mobile devices, with unprecedented processing power, storage capacity, and access to knowledge, are unlimited. People now can continuously produce new information and generate new knowledge in the mining of information.
Seedstars Values VS The Entrepreneurial Mindset
Having the right skills doesn’t always guarantee opportunities and success when you don’t have the right mentality. We have always heard about how entrepreneurs should be risk takers, and opportunity seekers, but through Seedstars values, Sabrina opened our eyes to a new side for the entrepreneurial mentality that doesn’t only focus on the surrounding opportunities, but also on the individual’s efficient productivity, critical thinking skills, and team cohesiveness mentality.
Hack the System
We have always heard the saying “Work Smarter Not Harder” and that’s what hacking the system means. To “Working smarter”, you will have to build as much experience as possible and put that accumulated experience into use to come up with new ways to get tasks done, that are faster, more efficient, and effective. Hacking the system requires one to have a fluid and flexible mentality, meaning that you will have to train your mind to think differently and find the loopholes in things that will get you to your desired outcomes faster, but how can you develop a flexible way of thinking?
Train Your Brain Muscles
Before diving deeper into the means of brain training, you have to understand the difference between a Fixed Mindset and a Growth Mindset.

I’m only good at certain things
I give up when it gets too hard
I hate challenges
I take feedback and criticism personally
I don’t like doing what I don’t know
I like learning about things I don’t know
I can be good at anything
I try until I get the results I want
I embrace challenges
I welcome feedback and criticism
10 Ways to Think Outside of the Box
- Question the status quo regularly
- Take a wider perspective
- Embrace uncommon/stupid/crazy ideas
- Draw
- Study other industries, read books/blogs, etc.
- Turn it upside down (put yourself on the other side of the table)
- Work backwards
- Ask a child for advice
- Invite randomness
- Take a shower
Get it Done
Getting it done is all about thinking about your tasks and categorizing them to what really moves you towards your objectives. Spending your energy and time on actions that will get you to your main goal faster!
Seedstars has adopted the Eisenhower Matrix, but what is it? How can it help you?
Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix is a productivity, prioritization, and time-management framework designed to help you prioritize a list of tasks or agenda items by first categorizing those items according to their urgency and importance.
For instance, items in quadrant 1 are urgent, so these should command your immediate attention. Tackling these items and crossing them off the list first ensures what was most pressing and important doesn’t get dropped. Only once everything in the first quadrant is finished—or taken as far as possible for the moment—should your gaze wander elsewhere.
This Matrix categorizes tasks under 4 main categories: the DO, the Plan, the Delegate, and the Delete.
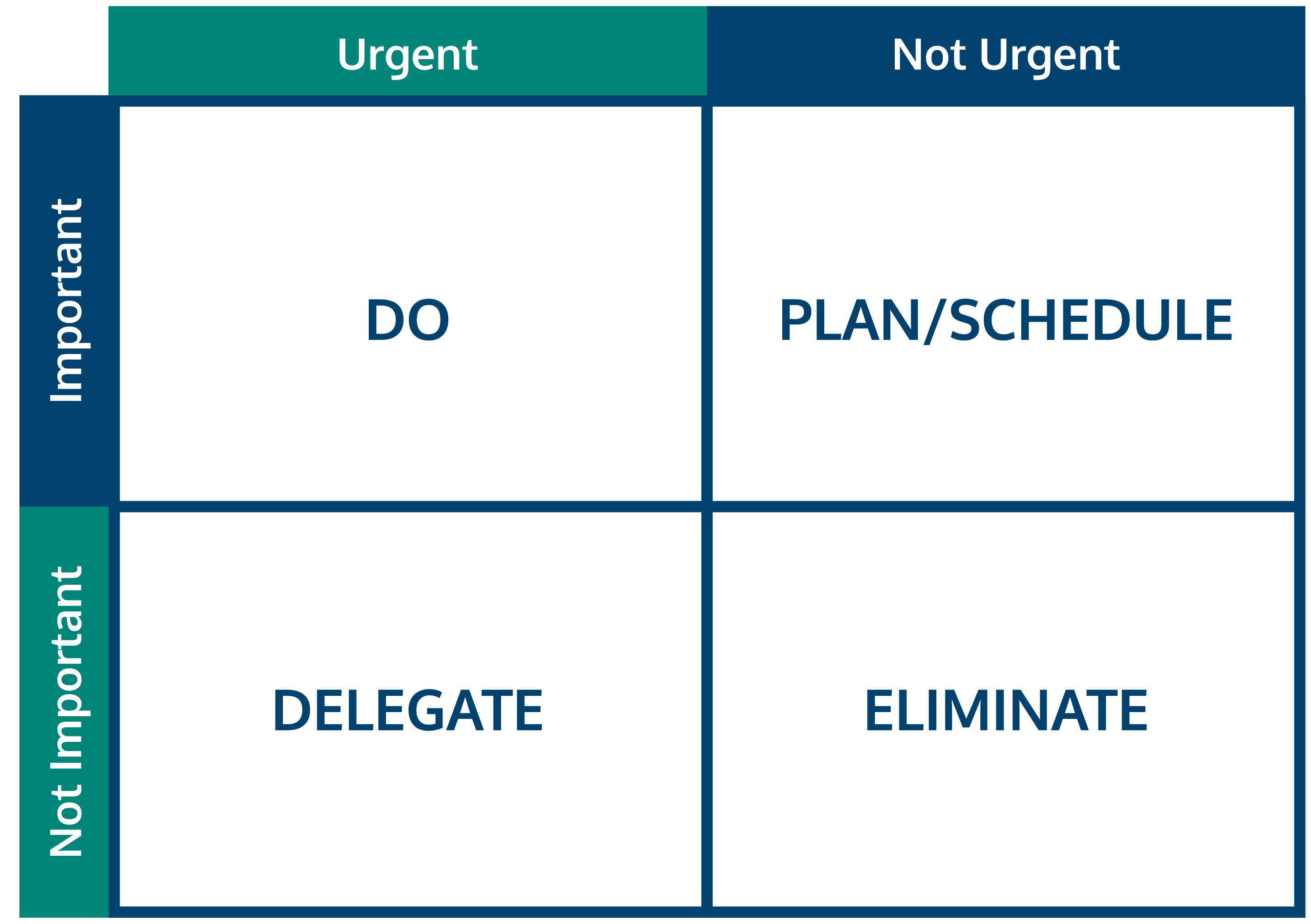
Do the tasks
These are the items that are both urgent and important, and they, therefore, demand your action right away. Items in this quadrant typically include crises and issues with deadlines. One example, the Business thinker Stephen Covey explains in his sample Eisenhower Matrix above, might be a fire in your kitchen.
Decide on when to deal with the tasks
These are essential issues, but they’re not urgent and therefore don’t require your immediate action. So these are the items you’ll want to schedule work for a later time. Quadrant 2 items are typically tasks that can help you personally or professionally or help your business achieve a long-term goal.
Delegate the tasks
These are urgent items that pop up and demand immediate attention. But are not necessary, and don’t necessarily require your time. Examples of these items would be requests for help from colleagues or emails marked urgent. If the content of these interruptions doesn’t rise to your level of importance, delegate them to others.
Delete the items
These items are not essential or urgent, so you can, in most cases, erase them from your list. Quadrant 4 items include scrolling through Facebook, checking Twitter, or playing games. These tasks are okay if you have time or need a break from the more important and more urgent items, but they should not displace them on your list of priorities.
The Eisenhower Matrix is primarily a tool for prioritization. It offers guidance for figuring out how individuals or teams should spend their time. As a lot of times, we spend our time on plenty of tasks with minimal impact, the Eisenhower Matrix acknowledges this and instead helps people make the most of the time they have.
In Experience We Trust
When we talk about this value, we must talk a bit about the science. In essence, this value is about how you work in a way that success becomes somehow predictable, or that at least can be engineered. Of course, there is always an element of luck, or starting skills and resources, but there is a method behind success.
You probably heard the saying “Practice makes perfect “at least ones in your life, through practice, we don’t keep doing the same thing over and over exactly the way you did the first time and get better at it. We get better as we keep experimenting with different approaches each time; testing, evaluating, collecting data, taking best practices from different fields, and testing again in order to build a solid methodology in which we can create the best outcomes. It’s not a one experiment that will build it all. You will never know exactly what made it accelerate. It’s an accumulation of experiments that make you pick off.
How To Adopt This Value in Your Company?

Data-driven diagnostic
What have I learned so far, and what do I still need to learn that is important?
Assumption-setting at the edge of current knowledge
At this stage, you will put your knowledge into work. Experiments have to be done in order to learn something truly new. To achieve that, you will have to starts with the right assumption before testing.
Time-limited & Scientific Testing
You have to think to yourself, how can I confirm my assumption in the shortest possible time frame to reach a reasonable confidence level? Your experiment must be time bound with a very scientific approach. That’s why it’s called an experiment.
Focused Learning
You cannot be learning to many dimensions at the same time. For examples, a basketball player cannot improve shooting, endurance, and passing, all at the same time and all in the same 100 hours.
To be able to benefit, you will need to focus on a highly specific and measurable skill at a time.
Implement Fiercely
Finally, once you learn, now you need to implement those learning as fearlessly and fiercely as possible and embed that learning faster and better than your competition. Experimenting is all about doing it better and faster. Finding your product, finding your niche, understand what matter at the very granular level and replicating across your organization.
Independently Together
This value follows the science of the wisdom of the crowd. To achieve the same objective, doesn’t mean you, and your teammates must be working together all the time.
“If you want to go fast, GO ALONE. If you want to go far, GO TOGETHER.“
- Ask for clarification, make sure you understand the final objective
- Take the initiative. Speak up, push if things don’t move
- Keep yourself accountable
- Have a (personal) vision of where you want to go. What is the career you want to have? How can Seedstars help you?
- Set your own agenda. Have a plan and stick to it. Stay committed
- Have courage to make bold declarations
7. Build your competence and gain the basic skills you need
8. Speak up! If you see something is not right / it can be improved
9. Have empathy and understanding
10. Have a servant’s heart. Help without expecting something in return.
11. Pay attention to others
12. Get the ball rolling
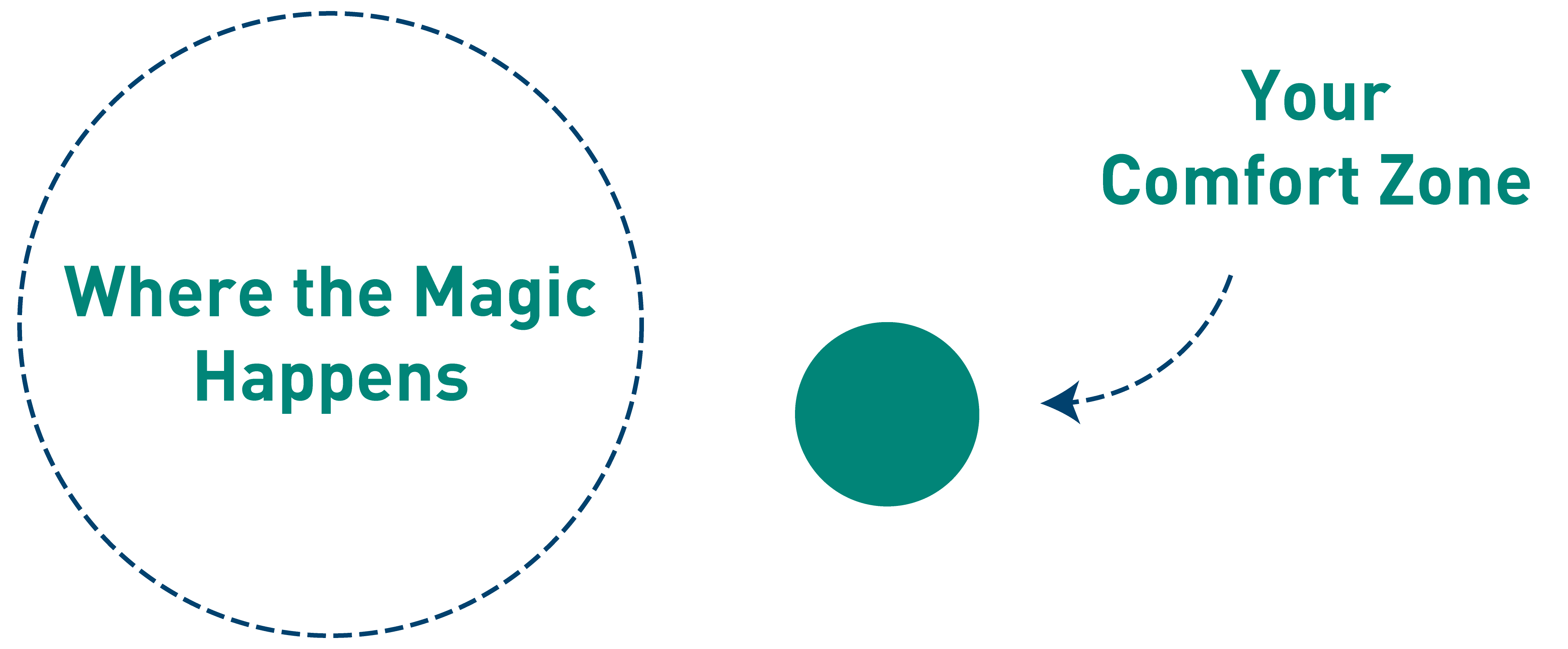
Getting Out of Your Comfort Zone
Getting comfortable with the uncomfortable. The best way to have a thermometer do measure your status within the comfort zone is your number of failures. If you are not failing enough, then it probably means that you are not experimenting with new approaches.
Follow The Money
If your startup is impact driven, it does not mean you that it cannot be profit-driven. Profit and purpose can come hand-in-hand.
This value can be seen quite aggressive. In the entrepreneurial mindset, its quite important because you must be comfortable with money. Ultimately, we align with the fact that money is a key indicator so that the machine can grow. Generate cash will make you scale.

Keep it Swiss
When you think about Switzerland, you think of the quality of the Swiss watches, or the trains that are always on time. Quality and precision are exactly what this value is about: It’s about delivering quality in everything you do and delivering on time. It is about attention to detail, and about doing clean work and being professional. To be able to do that, you need to continuously be perfecting the processes within your startup and keeping them up to date.
We talked about the Hack the System value earlier. You might think that these values are contradictory and there is tension between them. So how do you choose which one to use? You can ask yourself a key question: Who is the client? Is it an external client? What is the minimum level of quality expected? What is the best pragmatic approach that we as company can follow to move in the right direction?
For example: You can Hack the System when building quick MVPs to validate a feature on your app with test users. It doesn’t need to be perfect, but once you roll out that feature fully, this is where you Keep It Swiss. It has to be flawless, and has to work perfectly without crashing and without being buggy So it’s up to you to decide what level of KeepItSwiss and HackTheSystem you have to follow.
No Excuses
This value is about self-accountability, it’s about keeping your promises and the commitments you make to yourself, to your colleagues and to external partners or clients.
Finding the right balance between the skills of tomorrow, and Seedstars values, will result in an ever-growing innovative and productive efforts that suites our ever-growing future. Going back to the value of Independently Together. It only works if the team adopts the No Excuse value, because others depend on us to deliver on our promises.
This value is not about avoiding mistakes or about becoming inflexible (deliver or else). The spirit of it is to help us take our commitments seriously, and we see it necessarily in an environment where there is a lot of focus on autonomy and freedom which is usually the case with startups, and in which you don’t want to put individual tracking and controlling mechanisms in place, and where the role of the leaders is not to “supervise”, but to inspire and lead others.
